2. From PE to Memory
Memory Layout: How the Code Moves
sequenceDiagram
participant Memory as PE File Memory
participant Program as Parsing Code
Program->>Memory: Read IMAGE_NT_HEADERS
Program->>Memory: Locate Section Headers
loop For Each Section
Program->>Memory: Read Section Name and Properties
Program->>Memory: Compute RVA and File Offset
end
Program->>Memory: Complete Section ParsingBinary Traversal: Pointer Arithmetic
graph LR
A[Base Address of PE File] -->|Read IMAGE_NT_HEADERS| B[IMAGE_NT_HEADERS]
B -->|Move by sizeof IMAGE_NT_HEADERS| C[First Section Header]
C -->|Move by sizeof IMAGE_SECTION_HEADER| D[Second Section Header]
D -->|Move by sizeof IMAGE_SECTION_HEADER| E[Third Section Header]
E -->|Continue for all Sections| F[End of Section Headers]Explanation of Execution
- The PE file is loaded into memory.
- The program reads the PE headers: IMAGE_DOS_HEADER and IMAGE_NT_HEADERS.
- It locates the start of section headers by skipping IMAGE_NT_HEADERS.
- A loop iterates through sections, moving from one IMAGE_SECTION_HEADER to the next.
- Each section's metadata is extracted, such as:
- Name
.text,.data,.rsrc,.reloc - Virtual Address
- Size of Raw Data
- Characteristics: Executable, Readable, Writable
- Name
- Execution completes after parsing all sections.
https://fluxsec.red/rust-edr-evasion-hells-gate
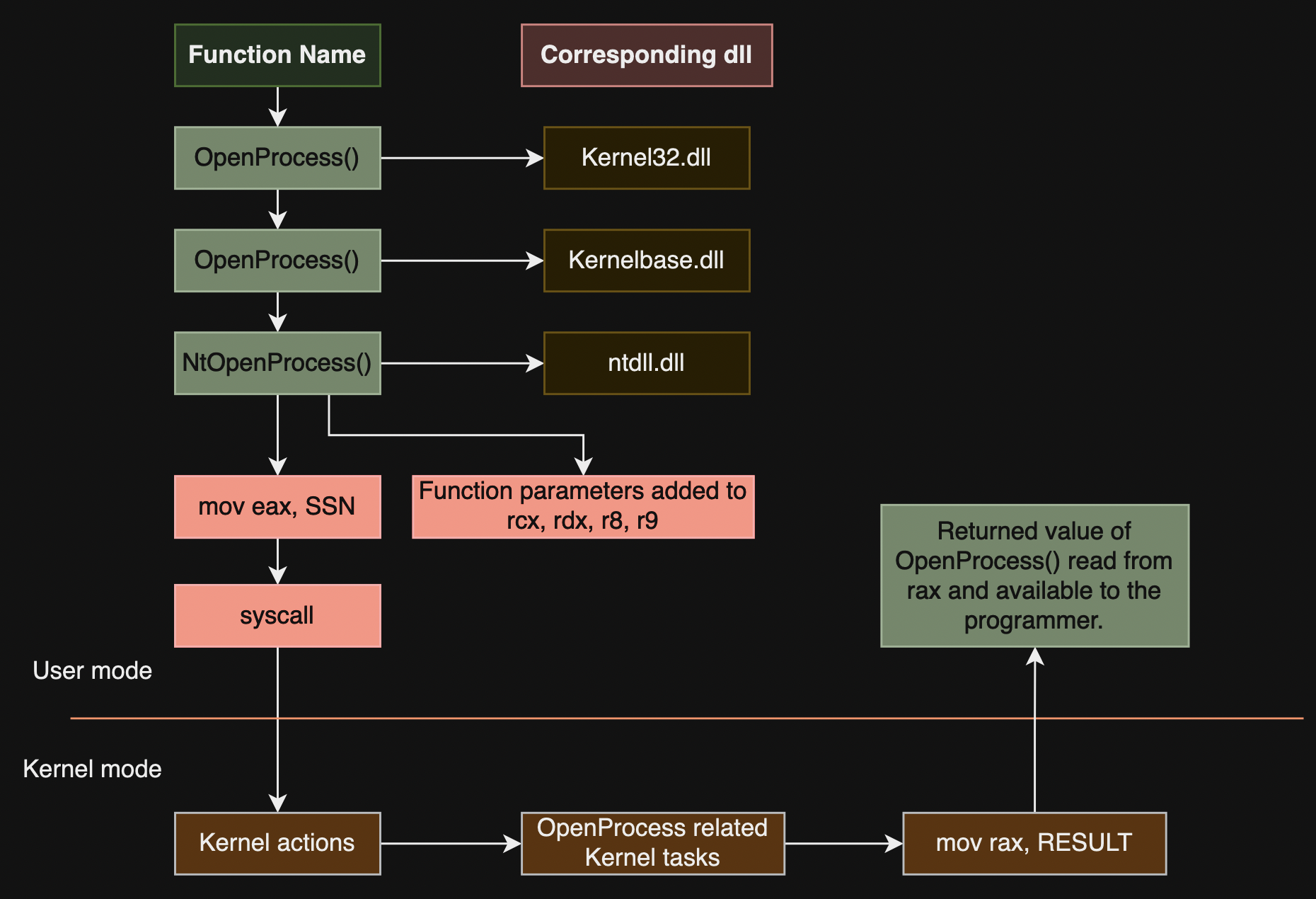

graph TD
A[User Application] -->|Calls Function| B[Win32 API - kernel32.dll / user32.dll]
B -->|Calls Function| C[Ntdll.dll - Native API]
C -->|Executes Syscall Instruction| D[Windows Kernel - KiSystemService]
D -->|Handles Request| E[Kernel-Mode Service - ntoskrnl.exe]
E -->|Returns Result| D
D -->|Returns to User Mode| C
C -->|Returns Result| B
B -->|Returns to Application| A